Before talking about phases of compiler let me try to give an idea of Phases.
Phases: Phases are the logically interrelated operation that takes source program in one representation and produces output in another representation.
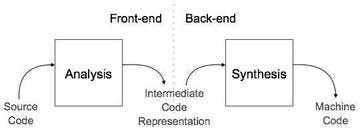
There are two major phases of a compiler:
Analysis Phase:
- Machine independent
- Language dependent
- Analysis phase creates an intermediate representation from the given source code.
Synthesis Phase:
- Machine dependent
- Language independent
- Synthesis phase creates an equivalent target program from the intermediate representation.
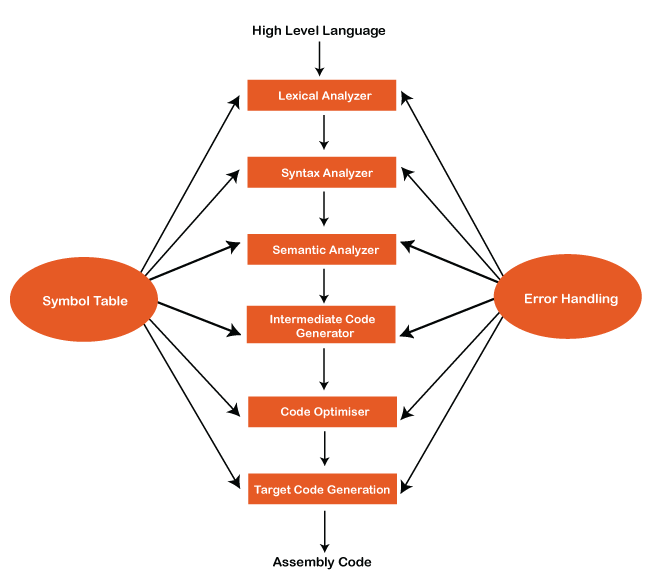
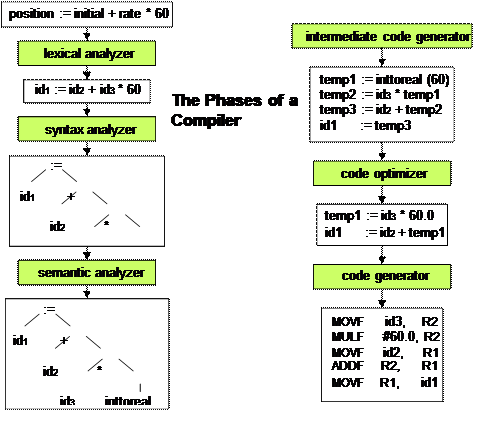
Lexical Analyzer: It is also called Scanner.
- It takes the output of the preprocessor as the input which is in a pure high-level language. It reads the characters from the source program and groups them into lexemes (sequence of characters that “go together”). Each lexeme corresponds to a token. Tokens are defined by regular expressions which are understood by the lexical analyzer. It also removes lexical errors (for e.g., erroneous characters), comments, and white space.
- This is Analysis Phase.
Syntax Analyzer: It is also called Parser. Because It constructs Parse Tree.
- It takes all tokens one by one and uses Context Free Grammer to construct the parse tree.
- This is Analysis Phase.
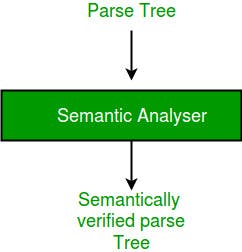
Semantic Analyzer: It verifies the Parse tree which we get from Syntax Analyzer.
- It checks if it is meaningful or not, and produces a verified parse tree.
- It also checks type checking, label checking, and flow control checking.
- This is Analysis Phase.
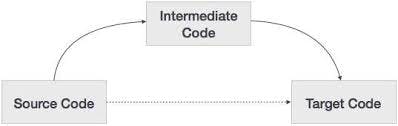
Intermediate Code Generator: It generate intermediate code.
- This phase is bridges the analysis and synthesis phase of translation.
- In this phase, we convert our code into low-level language.
Code Optimizer: It transfers code so that it consumes fewer resources and produces more speed. The meaning of the code being transformed is not altered.
- Optimization can be categorized into two types:
- Machine independent
- Machine dependent
- Optimization can be categorized into two types:
Target Code Generator: This is the final stage of compilation.
- It takes the output of Code Optimizer and converts it into the sequence of relocatable machine code.
- Note: Your suggestion and feedback are welcome.